Fundamental Statistical Methods for Engineers

In today’s data-rich engineering environments, a solid grasp of fundamental statistical methods is essential. Engineers routinely face variability in materials, processes, and measurements — and statistics provides the tools to understand, model, and c …
Fundamental Statistical Tools

This workshop offers an introduction to the fundamental principles and concepts in statistics. The first part covers classical and more recent exploratory data analysis (EDA) techniques to describe data with numerical and graphical tools. The various uses of these methods such as outlier detection is discussed. The second part addresses, with the help of real-life examples, the principles underlying statistical testing and decision-making in the presence of uncertainty. It covers risks involved, effect size, p-values as well as statistical significance and practical relevance. The use and interpretation of confidence intervals is also discussed. An excellent introductory module and a solid basis for all other courses.
Outils statistiques pour la R&D

Cet atelier propose une introduction aux principes et concepts fondamentaux de la statistique. La première partie couvre les techniques classiques et plus récentes d’analyse exploratoire des données (EDA) pour décrire les données avec des outils numériques et graphiques. Les différentes utilisations de ces méthodes telles que la détection des valeurs aberrantes sont abordées. La deuxième partie aborde, à l’aide d’exemples concrets, les principes sous-jacents aux tests statistiques et à la prise de décision en présence d’incertitude. Elle couvre les risques encourus, la taille de l’effet, les valeurs p ainsi que la signification statistique et la pertinence pratique. L’utilisation et l’interprétation des intervalles de confiance sont également abordées. Un excellent module d’introduction et une base solide pour tous les autres cours.
Masterclass: Best Statistical Practices for the Life Sciences

A 3-hour workshop during which the key elements of the recommendations and regulations of the various government agencies (Health Canada, FDA, EMA, etc.) are presented with their concrete implications on the practices to be respected. Aimed at both management teams and scientific staff, the workshop allows stakeholders to be made aware of these issues. In itself, the workshop is sufficient to allow startups to self-assess their practices and offer them tools to improve the points they consider problematic.
Masterclass : meilleures pratiques statistiques en sciences de la vie

Un atelier de 3 heures au cours duquel sont présentés les éléments clés des recommandations et réglementations des différentes agences gouvernementales (Santé Canada, FDA, EMA, etc.) avec leurs implications concrètes sur les pratiques à respecter. S’adressant aussi bien aux équipes de direction qu’au personnel scientifique, l’atelier permet de sensibiliser les parties prenantes à ces enjeux. En soi, l’atelier est suffisant pour permettre aux startups d’autoévaluer leurs pratiques et leur proposer des outils pour améliorer les points qu’elles jugent problématiques.
Two Serious Games to Understand the Role of Statistics in R&D

Stimulate innovation in R&D with our two collaborative serious games on statistical best practices. Participate in DataQuest & InnovaStat to understand the role of statistics in R&D. Designed for R&D, clinical, regulatory, and managerial teams, our games promote cross-functionality, collective decision-making, and the practical appropriation of key statistical concepts.
Deux jeux sérieux pour appréhender le rôle de la statistique en R&D v2

Stimulez l’innovation en R&D avec nos 2 jeux sérieux collaboratifs sur les bonnes pratiques statistiques. Participez à DataQuest et InnovaStat pour appréhender le rôle de la statistique en R&D. Conçus pour les équipes R&D, cliniques, réglementaires ou managériales, nos jeux favorisent la transversalité, la prise de décision collective et l’appropriation concrète des concepts statistiques clés.
Biostatistics in the Medical Literature

Become more confident when discussing clinical results with leading healthcare providers. This course covers key biostatistical concepts required to review and interpret findings published in the biomedical literature. The exact course curriculum is tailored to the therapy area of interest. Selected scientific publications are reviewed, discussed and criticised.
Biostatistique en recherche médicale

Gagnez en confiance lors de la discussion des résultats cliniques avec les principaux prestataires de soins de santé. Ce cours couvre les concepts biostatistiques clés nécessaires à l’examen et à l’interprétation des résultats publiés dans la littérature biomédicale. Le programme exact du cours est adapté au domaine thérapeutique concerné. Des publications scientifiques sélectionnées sont examinées, discutées et critiquées.
Engineering Applications of Machine Learning

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a prominent sale argument no matter whether you want to buy a simple toaster or an advanced assembly line robot. The purpose of this seminar is to demystify the jargon used and to provide attendees with the tools …
Applications de l’apprentissage automatique en ingénierie

L’intelligence artificielle (IA) est devenue un argument de vente de premier plan, que vous souhaitiez acheter un simple grille-pain ou un robot de chaîne de montage avancé. L’objectif de ce séminaire est de démystifier le jargon utilisé et de fournir …
Introduction to the Design of Experiments ‘DOE’

Variation is present in every experiment. Learn about DoE techniques to control variation, and to maximise data quality. This workshop presents classical techniques to design efficient experiments as well as the tools to analyze their results. The principles of sample size calculations, strategies to remove undesirable sources of variability like the use of blocks and controls, as well as the most commonly used experimental designs are discussed. The statistical analysis of designed experiments is progressively introduced, starting with the t-test method used to compare two groups. Then, the analysis of variance technique (ANOVA) is extensively covered from simple one-factor experiments to more advanced multi-factor situations where the interaction between factors needs to be considered. Multiple comparisons techniques used to locate differences are also presented.
Introduction à la planification d’expériences

La variation est présente dans chaque expérience. Découvrez les techniques DoE pour contrôler la variation et maximiser la qualité des données. Cet atelier présente les techniques classiques pour concevoir des expériences efficaces ainsi que les outils pour analyser leurs résultats. Les principes de calcul de la taille de l’échantillon, les stratégies pour éliminer les sources indésirables de variabilité comme l’utilisation de blocs et de contrôles, ainsi que les plans d’expériences les plus couramment utilisés sont abordés. L’analyse statistique des expériences planifiées est progressivement couverte du test t utilisée à l’analyse de la variance (ANOVA).
Advanced Experimental Designs

Learn about advanced experimental designs to account for experimental various types of constraints such as time, available resources, material heterogeneity, randomization restrictions when certain factors are more difficult or costly to change than others, different sizes of experimental units as well as repeated measures. In this course, the construction of advanced designs and their statistical analysis is covered with the help of real case studies.
Planification d’expériences avancée

Apprenez les plans d’expérience avancés pour tenir compte de divers types de contraintes expérimentales telles que le temps, les ressources disponibles, l’hétérogénéité des matériaux, les restrictions de randomisation lorsque certains facteurs sont plus difficiles ou coûteux à modifier que d’autres, les différentes tailles d’unités expérimentales ainsi que les mesures répétées. Dans ce cours, la construction de plans d’expérience avancés et leur analyse statistique sont abordées à l’aide d’études de cas réels.
Analyse statistique des données métagénomiques

Les données métagénomiques présentent des caractéristiques spécifiques qui nécessitent des méthodes statistiques adaptées. Découvrez les outils statistiques les plus couramment utilisés dans ce domaine. La formation débute par un rappel des tests d’hypothèses, des risques associés, de la multiplicité et de la manière de les contrôler. Apprenez ensuite quelles sont les spécificités et les problématiques des données génomiques. La formation revient sur les tests classiques de comparaison de groupes (ANOVA, MANOVA) et leur extension aux tests adaptés aux données génomiques (ANOSIM et PERMANOVA). Les outils de visualisation des données et le choix d’une métrique de distance sont également abordés.
Statistical Analysis of Metagenomics Data

Metagenomic data have specific characteristics that require adapted statistical methods. Discover the most commonly used statistical tools in this field. The training begins with a reminder of hypothesis testing, associated risks, multiplicity and how to control them. Then learn what are the specificities and problems of genomic data. The training reviews classic tests for comparing groups (ANOVA, MANOVA) and their extension to tests adapted to genomic data (ANOSIM and PERMANOVA). Data visualization tools and choice of a distance metric are also discussed.
Linear Regression Modelling Techniques

The linear regression is a method used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables by fitting a linear equation to observed data. Building a regression model with stats packages has become straightforward. However, interpreting the software output and building a good model are no simple tasks. Learn about statistical modeling with a focus on linear models. What is a model? Estimating and interpreting model coefficients. Dealing with continuous and categorical predictors and interactions. Evaluating model performance: explanatory vs. predictive. Common pitfalls and best practices.
Techniques de modélisation: la régression linéaire

La régression linéaire est une méthode utilisée pour modéliser la relation entre une variable dépendante et une ou plusieurs variables indépendantes en ajustant une équation linéaire aux données observées. La création d’un modèle de régression avec des logiciels statistiques est devenue simple. Cependant, l’interprétation des résultats du logiciel et la création d’un bon modèle ne sont pas des tâches simples. Découvrez la modélisation statistique en mettant l’accent sur les modèles linéaires. Qu’est-ce qu’un modèle ? Estimation et interprétation des coefficients du modèle. Gestion des prédicteurs et des interactions continus et catégoriels. Évaluation des performances du modèle : explicatif ou prédictif. Pièges courants et meilleures pratiques.
Screening Techniques in DOE

In preliminary research phases, the number of potentially influential factors to investigate is usually large. Screening designs are experimental designs used to identify the most influential factors that influence a response or outcome in a process or system with a reasonable number of runs. These designs are typically used in the early stages of experimentation, when you want to quickly assess a large number of variables to determine which ones have the greatest effect on the response variable. The goal is to eliminate unimportant factors and focus resources on the most influential ones. Learn about the construction of fractional factorial designs, aliasing and de-aliasing strategie. A working knowledge of multiple linear regression is needed to make the most out of this workshop.
Plans de criblage

Dans les phases préliminaires de recherche, le nombre de facteurs potentiellement influents à étudier est généralement important. Les plans de sélection sont des plans expérimentaux utilisés pour identifier les facteurs les plus influents qui influencent une réponse ou un résultat dans un processus ou un système avec un nombre raisonnable d’exécutions. Ces plans sont généralement utilisés dans les premières étapes de l’expérimentation, lorsque vous souhaitez évaluer rapidement un grand nombre de variables pour déterminer celles qui ont le plus d’effet sur la variable de réponse. L’objectif est d’éliminer les facteurs sans importance et de concentrer les ressources sur les plus influents. Découvrez la construction de plans factoriels fractionnaires, les stratégies d’aliasing et de de-aliasing. Une connaissance pratique de la régression linéaire multiple est nécessaire pour tirer le meilleur parti de cet atelier.
Optimisation Designs

Optimization designs refer to experimental design strategies that are specifically structured to optimize a process, product, or system. The goal of these designs is to identify the combination of factors (inputs) that lead to the best possible outcome (response) according to a defined objective, such as maximizing performance, minimizing cost, or finding the most efficient operating conditions. Learn more about experimental designs when influential factors have been identified and the goal is to optimize their levels. Principle underlying the construction of composite and Box-Behnken design are covered. Principle, model-building, and response surface methodology are reviewed.
Plans pour l’optimisation

Les plans d’optimisation font référence à des stratégies de conception expérimentale spécifiquement structurées pour optimiser un processus, un produit ou un système. L’objectif de ces plans est d’identifier la combinaison de facteurs (entrées) qui conduisent au meilleur résultat possible (réponse) selon un objectif défini, tel que maximiser les performances, minimiser les coûts ou trouver les conditions de fonctionnement les plus efficaces. Apprenez-en davantage sur les plans expérimentaux lorsque des facteurs influents ont été identifiés et que l’objectif est d’optimiser leurs niveaux. Le principe sous-jacent à la construction de plans composites et Box-Behnken est abordé. Le principe, la construction de modèles et la méthodologie de surface de réponse sont examinés.
Regression Modelling Techniques for Categorical Data
Linear regression is inappropriate to model binary responses such as pass/fail, survived/died. Learn the principle of logistic regression part of the Generalized Linear Models along with its similarities with linear regression and its specific tools. Good practices for model-building and for assessing model goodness-of-fit are presented.
Modélisation de données catégoriques

La régression linéaire n’est pas adaptée à la modélisation de réponses binaires telles que réussite/échec, survie/décès. Découvrez le principe de la régression logistique faisant partie des modèles linéaires généralisés ainsi que ses similitudes avec la régression linéaire et ses outils spécifiques. De bonnes pratiques pour la construction de modèles et pour l’évaluation de l’adéquation des modèles sont présentées.
Shelf-Life & Stability Studies – Design & Analysis

Shelf-life data possess specific features so that their design and analysis require adapted statistical tools. This workshop uses a variety of case studies to present the most important aspects to consider for a sound determination of product shelf life. Starting from the assessment of the differences between shelf-life and stability studies, participants learn for each type of study how to design efficient experiments to determine the failure time of products accurately. The issues discussed include the timepoint selection, how to handle destructive testing, the experiment size and the choice of samples. The workshop also emphasizes the appropriate ways to analyze life data and to adequately interpret and communicate the results obtained. The principle of accelerated shelf-life testing (ASLT) along with the conditions for a successful use are discussed.
Design & Analysis of Survival Studies
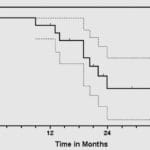
Lifetime data possess specific features so that their design and analysis require adapted statistical tools.This workshop uses a variety of case studies to present the most important aspects to consider for a sound determination of survival curves. Participants learn for each type of study how to design efficient experiments to determine the survival time of patients. The issues discussed include the timepoint selection, how to handle censoring (incomplete observations), competing risks, and the experiment size. The workshop also emphasizes the appropriate ways to analyze life data, how to compare curves, how to account for time-varying covariates and to adequately interpret and communicate the results obtained.
Études de durée de vie – Planification & analyse

Saviez-vous que les études de durée de vie possèdent des caractéristiques particulières qui nécessitent des outils statistiques adaptés? Découvrez-les pour la mise en place d’études efficaces et pour l’analyse adaptée des données.
Statistical Methods for Reliability Studies

Reliability studies are a type of research or experimental design focused on assessing and improving the reliability of systems, products, or processes. In these studies, the goal is to determine how consistently and dependably a system or product performs over time and under varying conditions. Reliability refers to the ability of a product, system, or component to function as intended without failure, across its expected lifespan or under specified conditions. In industrial applications, reliability is crucial and testing is expensive. Collected data must be exploited in the best way possible. Reliability data possess specific features that call for dedicated statistical methods. Learn about statistical tools for reliability analysis.
Méthodes statistiques pour les études de fiabilité

Dans les applications industrielles, la fiabilité est cruciale et les tests sont coûteux. Les données collectées doivent être exploitées de la meilleure façon possible. Les données de fiabilité possèdent des caractéristiques spécifiques qui nécessitent des méthodes statistiques dédiées. Découvrez les outils statistiques pour l’analyse de la fiabilité.
Principal Component Analysis

Learn about Principal Component Analysis, a data reduction technique, to identify, quantify & visualise the structure of a set of measurements. PCA provides insightful data visualisation tools. Learn about innovative applications. During the workshop, emphasis is put on the principles and the conditions of utilization of the method, the results they provide and their interpretation. Plenty of time is devoted to case studies and interpretation of software output.
Analyse en composantes principales – ACP

Découvrez l’analyse en composantes principales, une technique de réduction des données, pour identifier, quantifier et visualiser la structure d’un ensemble de mesures. L’ACP fournit des outils de visualisation de données perspicaces. Découvrez des applications innovantes. Au cours de l’atelier, l’accent est mis sur les principes et les conditions d’utilisation de la méthode, les résultats qu’ils fournissent et leur interprétation. Une grande partie du temps est consacrée aux études de cas et à l’interprétation des résultats du logiciel.
Cluster Analysis – Unsupervised Learning

Learn how to take data (consumers, genes, …) and organise them into homogeneous groups for use in many applications, such as market analysis and biomedical data analysis, or as a pre-processing step for many data mining tasks. Learn about this very active field of research in statistics and data mining, and discover new techniques. Learn about innovative applications. During the workshop, emphasis is put on the principles and the conditions of utilization of the method, the results they provide and their interpretation. Plenty of time is devoted to case studies and interpretation of software output.
Analyse de classification – apprentissage non-supervisé

L’analyse de classification – clustering – unsupervised learning – comprend un ensemble de techniques visant à regrouper des objects possédant des caractéristiques similaires: consommateurs, gènes, etc. C’est un champ de recherche très actif en statistique. Vous découvrirez les outils classiques ainsi que les récents développements.
